carbon dioxide is a nonpolar molecule Carbon dioxide co2 polar nonpolar structure bonds molecule bond look combined considered effect must let then these
Water is one of the most common substances on Earth and plays a crucial role in various biological and chemical processes. Understanding its properties, including whether it is polar or nonpolar, is fundamental in many scientific disciplines. In this post, we will delve into the polarity of water and explore its implications.
What is Polarity?
Polarity refers to the distribution of electric charge within a molecule. A polar molecule has regions of partial positive and partial negative charges due to the uneven distribution of electrons. On the other hand, a nonpolar molecule has an equal sharing of electrons, resulting in no specific or significant positive or negative regions.
The Polarity of Water
Water, H2O, is a polar molecule. This polarity arises due to the bent shape of the molecule and the difference in electronegativity between hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
 The oxygen atom in water is significantly more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms. As a result, the oxygen atom attracts the shared electrons more strongly, creating a partial negative charge (δ-) near the oxygen and partial positive charges (δ+) near the hydrogen atoms.
The oxygen atom in water is significantly more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms. As a result, the oxygen atom attracts the shared electrons more strongly, creating a partial negative charge (δ-) near the oxygen and partial positive charges (δ+) near the hydrogen atoms.
The Importance of Water’s Polarity
Water’s polarity plays a critical role in many chemical and biological processes. One of its most important properties is its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances. This property is crucial for the transport of nutrients and waste in living organisms.
 Water acts as a universal solvent due to its polarity. The partial positive charge on hydrogen atoms and the partial negative charge on oxygen atoms attract and surround charged or polar molecules, allowing them to dissolve in water. This makes water an excellent medium for chemical reactions and biological processes to occur.
Water acts as a universal solvent due to its polarity. The partial positive charge on hydrogen atoms and the partial negative charge on oxygen atoms attract and surround charged or polar molecules, allowing them to dissolve in water. This makes water an excellent medium for chemical reactions and biological processes to occur.
Additionally, water’s polarity gives rise to high surface tension and capillary action. Surface tension allows water to form droplets and maintain their shape, while capillary action enables water to climb against gravity in narrow spaces, such as plant roots.
Conclusion
In conclusion, water is a polar molecule, with oxygen being partially negative and hydrogen atoms partially positive. Its polarity is critical for a variety of chemical and biological processes, including dissolving substances and facilitating chemical reactions. Understanding the polarity of water provides insights into its unique properties and behavior, making it an essential topic in the study of various scientific disciplines.
If you are searching about Is Water Polar Or Nonpolar? - RankRed you’ve visit to the right place. We have 5 Images about Is Water Polar Or Nonpolar? - RankRed like Is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Polar Or Nonpolar? » Science ABC, Nonpolar Molecule Definition and Examples and also Nonpolar Molecule Definition and Examples. Read more:
Is Water Polar Or Nonpolar? - RankRed
 www.rankred.comnonpolar polar rankred atoms equally oxygen electronegative
www.rankred.comnonpolar polar rankred atoms equally oxygen electronegative
Chemical Bonds | Boundless Microbiology
 courses.lumenlearning.combonds microbiology covalent nonpolar chemical boundless polar bond molecule molecular type
courses.lumenlearning.combonds microbiology covalent nonpolar chemical boundless polar bond molecule molecular type
Is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Polar Or Nonpolar? » Science ABC
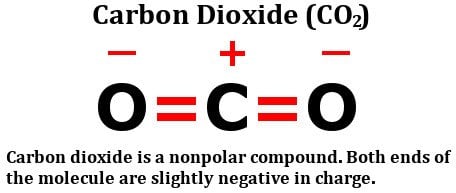 www.scienceabc.comcarbon dioxide co2 polar nonpolar structure bonds molecule bond look combined considered effect must let then these
www.scienceabc.comcarbon dioxide co2 polar nonpolar structure bonds molecule bond look combined considered effect must let then these
Symmetry - Why Is Carbon Dioxide A Non-polar Molecule? - Physics Stack
 physics.stackexchange.comco2 molecule polar carbon dioxide non why dipole moment charge vectors charges partial which vector zero cancel other negative positive
physics.stackexchange.comco2 molecule polar carbon dioxide non why dipole moment charge vectors charges partial which vector zero cancel other negative positive
Nonpolar Molecule Definition And Examples
/carbon-dioxide-molecule-545861181-5918b6765f9b586470f4575f.jpg) www.thoughtco.commolecule carbon dioxide nonpolar electron definition co2 example molekuul bonds domain examples linear science model alamy chemical domains vsepr formula
www.thoughtco.commolecule carbon dioxide nonpolar electron definition co2 example molekuul bonds domain examples linear science model alamy chemical domains vsepr formula
Is carbon dioxide (co2) polar or nonpolar? » science abc. Nonpolar polar rankred atoms equally oxygen electronegative. Bonds microbiology covalent nonpolar chemical boundless polar bond molecule molecular type